What Does Bradbury Bros Charge To Clean An Ac Condensate Line
Thunderstruck!

Where did the Australian rock ring AC/DC get their proper name from? Why, Alternating Electric current and Straight Current, of form! Both AC and DC describe types of current menstruum in a circuit. In directly current (DC), the electric charge (current) only flows in one direction. Electric charge in alternate current (Air conditioning), on the other paw, changes direction periodically. The voltage in Ac circuits as well periodically reverses because the current changes direction.
Well-nigh of the digital electronics that you build will use DC. However, it is important to understand some Ac concepts. Virtually homes are wired for Ac, and so if you programme to connect your Tardis music box project to an outlet, yous will need to convert Air-conditioning to DC. Ac also has some useful backdrop, such equally being able to convert voltage levels with a unmarried component (a transformer), which is why Ac was chosen as the primary means to transmit electricity over long distances.
What You Will Learn
- The history behind AC and DC
- Different ways to generate Air conditioning and DC
- Some examples of AC and DC applications
Recommended Reading
- What is Electricity
- What is a Excursion?
- Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm'south Police force
- Electric Power
Alternate Current (Air conditioning)
Alternating current describes the flow of charge that changes management periodically. Every bit a upshot, the voltage level as well reverses forth with the current. AC is used to deliver power to houses, office buildings, etc.
Generating AC
Ac can be produced using a device called an alternator. This device is a special type of electrical generator designed to produce alternate current.
A loop of wire is spun inside of a magnetic field, which induces a electric current along the wire. The rotation of the wire tin can come from any number of means: a wind turbine, a steam turbine, flowing water, and then on. Because the wire spins and enters a different magnetic polarity periodically, the voltage and current alternates on the wire. Hither is a short blitheness showing this principle:
(Video credit: Khurram Tanvir)
Generating Air-conditioning can be compared to our previous water analogy:
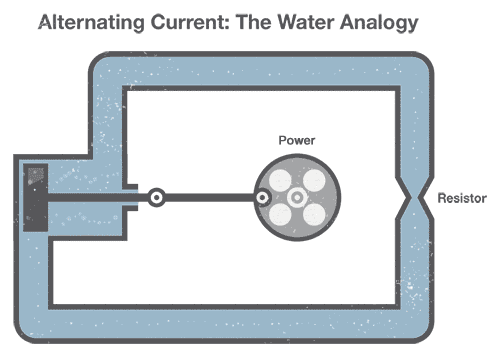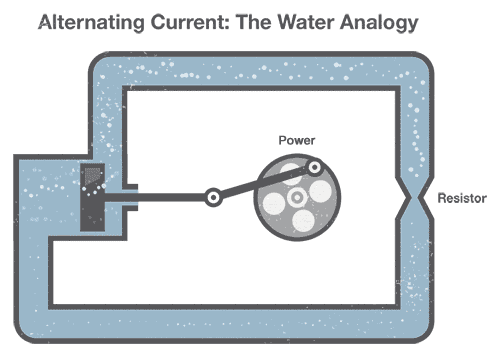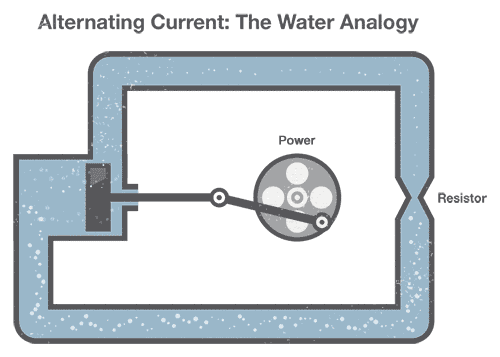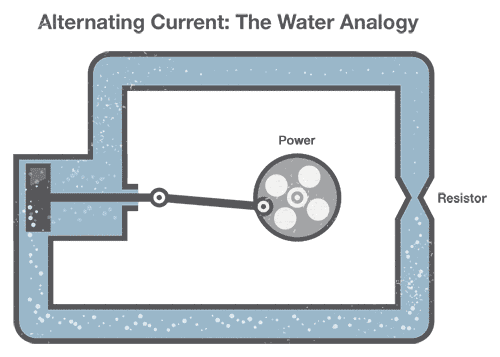
To generate Air-conditioning in a fix of water pipes, nosotros connect a mechanical creepo to a piston that moves water in the pipes dorsum and forth (our "alternating" electric current). Detect that the pinched section of pipe still provides resistance to the flow of water regardless of the direction of menses.
Waveforms
AC can come in a number of forms, as long as the voltage and current are alternating. If nosotros hook up an oscilloscope to a circuit with Air-conditioning and plot its voltage over time, we might run across a number of dissimilar waveforms. The most common type of Ac is the sine wave. The Ac in most homes and offices accept an aquiver voltage that produces a sine moving ridge.
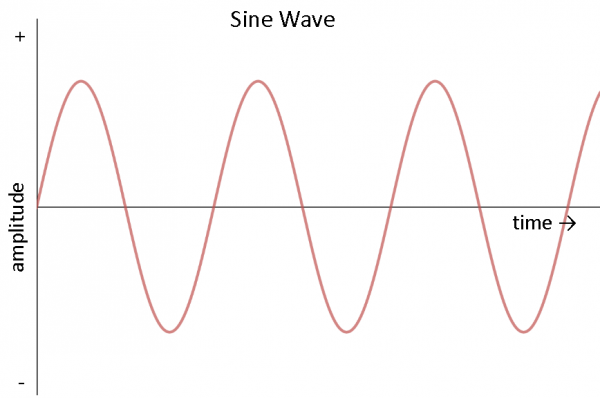
Other common forms of Air-conditioning include the square moving ridge and the triangle wave:
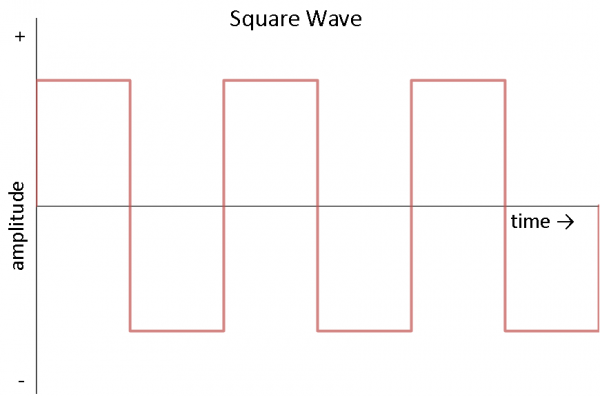
Square waves are often used in digital and switching electronics to examination their operation.
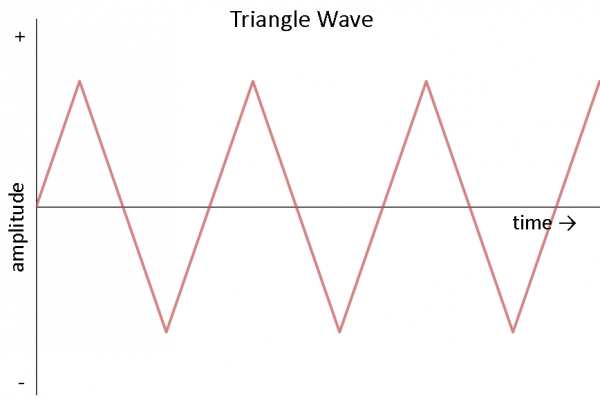
Triangle waves are found in audio synthesis and are useful for testing linear electronics like amplifiers.
Describing a Sine Wave
We often want to describe an AC waveform in mathematical terms. For this example, we will use the common sine moving ridge. There are three parts to a sine wave: amplitude, frequency, and stage.
Looking at just voltage, we can describe a sine wave as the mathematical part:
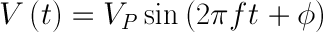
V(t) is our voltage as a function of time, which means that our voltage changes every bit time changes. The equation to the right of the equals sign describes how the voltage changes over time.
VP is the aamplitude. This describes the maximum voltage that our sine wave can achieve in either direction, meaning that our voltage can exist +VP volts, -VP volts, or somewhere in between.
The sin() function indicates that our voltage will be in the form of a periodic sine wave, which is a smooth oscillation effectually 0V.
2π is a constant that converts the freqency from cycles (in hertz) to athwart frequnecy (radians per 2nd).
f describes the frequency of the sine wave. This is given in the class of hertz or units per 2nd. The frequency tells how many times a particular wave form (in this case, one bicycle of our sine wave - a rise and a fall) occurs inside i second.
t is our independent variable: time (measured in seconds). As fourth dimension varies, our waveform varies.
φ describes the phase of the sine wave. Stage is a mensurate of how shifted the waveform is with respect to time. It is often given equally a number betwixt 0 and 360 and measured in degrees. Because of the periodic nature of the sine wave, if the moving ridge course is shifted by 360° information technology becomes the same waveform again, as if it was shifted past 0°. For simplicity, we sill assume that phase is 0° for the remainder of this tutorial.
We tin can turn to our trusty outlet for a proficient example of how an AC waveform works. In the Usa, the ability provided to our homes is Air-conditioning with nearly 170V nada-to-peak (amplitude) and 60Hz (frequency). Nosotros can plug these numbers into our formula to become the equation (remember that we are bold our phase is 0):
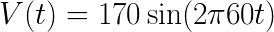
Nosotros can use our handy graphing calculator to graph this equation. If no graphing estimator is available we can use a gratuitous online graphing program like Desmos (Note that you might have to utilise 'y' instead of 'v' in the equation to meet the graph).
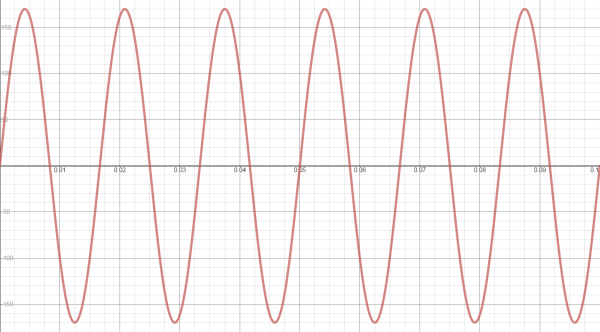
Notice that, as we predicted, the voltage ascension upward to 170V and downward to -170V periodically. Additionally, 60 cycles of the sine wave occurs every second. If we were to mensurate the voltage in our outlets with an oscilloscope, this is what nosotros would see (Alert: do not attempt to mensurate the voltage in an outlet with an oscilloscope! This will likely impairment the equipment).
NOTE: You might have heard that Air conditioning voltage in the US is 120V. This is also correct. How? When talking about Ac (since the voltage changes constantly), it is often easier to apply an average or mean. To accomplish that, we use a method called "Root mean squared." (RMS). Information technology is often helpful to use the RMS value for Air-conditioning when you want to calculate electrical ability. Fifty-fifty though, in our example, we had the voltage varying from -170V to 170V, the root mean square is 120V RMS.
Applications
Domicile and part outlets are almost e'er Air conditioning. This is because generating and transporting AC across long distances is relatively easy. At high voltages (over 110kV), less energy is lost in electric power transmission. Higher voltages mean lower currents, and lower currents mean less oestrus generated in the electric line due to resistance. Ac can exist converted to and from loftier voltages easily using transformers.
Air conditioning is as well capable of powering electric motors. Motors and generators are the exact same device, but motors catechumen electrical free energy into mechanical energy (if the shaft on a motor is spun, a voltage is generated at the terminals!). This is useful for many large appliances like dishwashers, refrigerators, then on, which run on AC.
Direct Current (DC)
Directly electric current is a bit easier to understand than alternating current. Rather than oscillating back and forth, DC provides a constant voltage or electric current.
Generating DC
DC can exist generated in a number of ways:
- An AC generator equipped with a device called a "commutator" tin produce straight current
- Use of a device called a "rectifier" that converts AC to DC
- Batteries provide DC, which is generated from a chemical reaction inside of the battery
Using our water analogy again, DC is similar to a tank of water with a hose at the end.

The tank can just push water ane manner: out the hose. Like to our DC-producing bombardment, once the tank is empty, water no longer flows through the pipes.
Describing DC
DC is defined every bit the "unidirectional" menstruation of current; current only flows in i direction. Voltage and current tin can vary over time so long as the direction of flow does not modify. To simplify things, nosotros will assume that voltage is a constant. For case, we assume that a AA battery provides 1.5V, which tin be described in mathematical terms as:
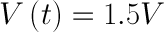
If we plot this over time, we see a constant voltage:
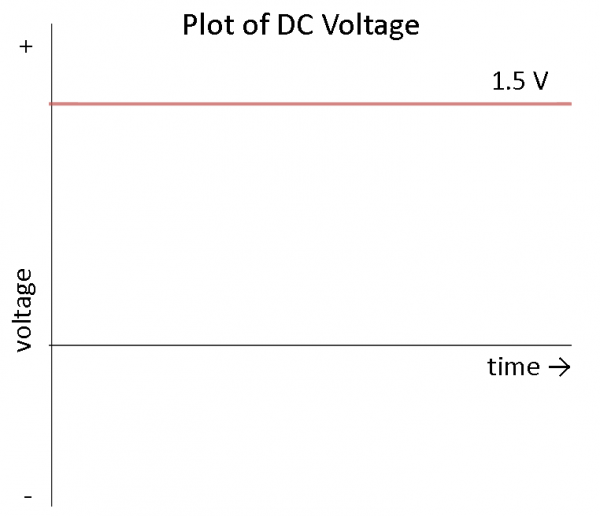
What does this mean? It means that nosotros can count on most DC sources to provide a constant voltage over fourth dimension. In reality, a battery will slowly lose its charge, meaning that the voltage volition drop every bit the bombardment is used. For most purposes, we tin assume that the voltage is abiding.
Applications
Almost all electronics projects and parts for sale on SparkFun run on DC. Everything that runs off of a bombardment, plugs in to the wall with an Air-conditioning adapter, or uses a USB cable for power relies on DC. Examples of DC electronics include:
- Cell phones
- The LilyPad-based D&D Dice Gauntlet
- Flat-screen TVs (AC goes into the TV, which is converted to DC)
- Flashlights
- Hybrid and electric vehicles
Battle of the Currents
Almost every habitation and business is wired for Air-conditioning. However, this was non an overnight decision. In the late 1880s, a diverseness of inventions across the Us and Europe led to a full-scale battle betwixt alternating current and straight electric current distribution.
In 1886, Ganz Works, an electric visitor located in Budapest, electrified all of Rome with Air-conditioning. Thomas Edison, on the other manus, had constructed 121 DC power stations in the Us by 1887. A turning signal in the boxing came when George Westinghouse, a famous industrialist from Pittsburgh, purchased Nikola Tesla's patents for Air-conditioning motors and transmission the adjacent year.
Air conditioning vs. DC

Thomas Edison (Image courtesy of biography.com)
In the late 1800s, DC could not be easily converted to high voltages. As a result, Edison proposed a system of pocket-sized, local power plants that would ability individual neighborhoods or city sections. Power was distributed using three wires from the power institute: +110 volts, 0 volts, and -110 volts. Lights and motors could be connected between either the +110V or 110V socket and 0V (neutral). 110V immune for some voltage drop between the plant and the load (home, function, etc.).
Even though the voltage drop across the power lines was accounted for, power plants needed to be located within 1 mile of the end user. This limitation made power distribution in rural areas extremely difficult, if non impossible.
With Tesla's patents, Westinghouse worked to perfect the Air-conditioning distribution organisation. Transformers provided an inexpensive method to step up the voltage of AC to several chiliad volts and back downwardly to usable levels. At college voltages, the same ability could be transmitted at much lower current, which meant less power lost due to resistance in the wires. Equally a result, large power plants could be located many miles away and service a greater number of people and buildings.
Edison's Smear Campaign
Over the side by side few years, Edison ran a campaign to highly discourage the use of AC in the Us, which included lobbying state legislatures and spreading disinformation about AC. Edison likewise directed several technicians to publicly electrocute animals with AC in an endeavour to testify that Air-conditioning was more than dangerous than DC. In effort to display these dangers, Harold P. Brown and Arthur Kennelly, employees of Edison, designed the first electric chair for the state of New York using Ac.
The Ascension of AC
In 1891, the International Electro-Technical Exhibition was held in Frankfurt, Germany and displayed the first long distance transmission of iii-phase Air-conditioning, which powered lights and motors at the exhibition. Several representatives from what would become General Electric were present and were subsequently impressed by the display. The post-obit year, Full general Electric formed and began to invest in Air-conditioning technology.
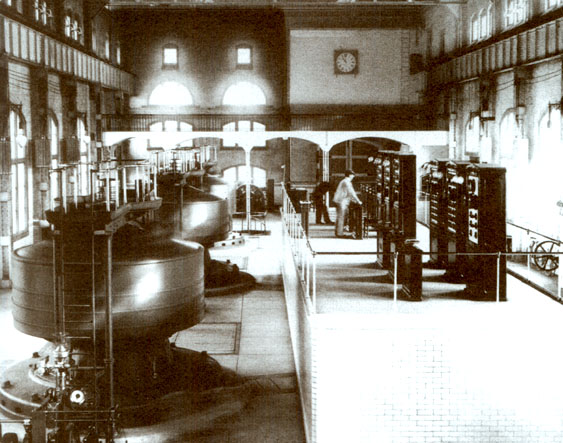

Edward Dean Adams Power Plant at Niagara Falls, 1896 (Paradigm courtesy of teslasociety.com)
Westinghouse won a contract in 1893 to build a hydroelectric dam to harness the power of Niagara falls and transmit AC to Buffalo, NY. The project was completed on November 16, 1896 and AC power began to ability industries in Buffalo. This milestone marked the reject of DC in the United States. While Europe would adopt an Air-conditioning standard of 220-240 volts at 50 Hz, the standard in North America would get 120 volts at 60 Hz.
High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC)
Swiss engineer René Thury used a serial of motor-generators to create a high-voltage DC system in the 1880s, which could be used to transmit DC ability over long distances. However, due to the high cost and maintenance of the Thury systems, HVDC was never adopted for almost a century.
With the invention of semiconductor electronics in the 1970s, economically transforming between AC and DC became possible. Specialized equipment could be used to generate high voltage DC power (some reaching 800 kV). Parts of Europe have begun to employ HVDC lines to electrically connect various countries.
HVDC lines experience less loss than equivalent Ac lines over extremely long distances. Additionally, HVDC allows different AC systems (due east.g. 50 Hz and 60 Hz) to exist connected. Despite its advantages, HVDC systems are more costly and less reliable than the mutual Air conditioning systems.
In the end, Edison, Tesla, and Westinghouse may have their wishes come true. AC and DC can coexist and each serve a purpose.
Resources and Going Further
You should now take a skillful understanding of the differences betwixt Ac and DC. Air-conditioning is easier to transform between voltage levels, which makes high-voltage transmission more than viable. DC, on the other hand, is found in almost all electronics. Y'all should know that the two do not mix very well, and you volition demand to transform Air-conditioning to DC if y'all wish to plug in well-nigh electronics into a wall outlet. With this understanding, y'all should exist fix to tackle some more complex circuitry and concepts, even if they contain AC.
Take a expect at the following tutorials when you are ready to dive deeper into the earth of electronics:
- Series and Parallel Circuits
- Logic Levels
- How to Use a Multimeter
- How to Power a Projection
Source: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/alternating-current-ac-vs-direct-current-dc/all
Posted by: macksorece.blogspot.com



0 Response to "What Does Bradbury Bros Charge To Clean An Ac Condensate Line"
Post a Comment